Marcian Hoff : An Electrical Engineer Who Co-invented the First Microprocessor
The modification of an already existing invention is much easier than proposing the idea of creating a new one. With time, advancement in technology and acceptance within mankind both took place, which seemed like far-fetched goals in the earlier days. Even though there were many obstacles in the past, many significant scientists emerged out on the surface with innovative innovations. And, today, these are the innovations that are helping us take a step forward towards building a smarter world.
Marcian Hoff, popularly known as Ted Hoff, is one such brilliant innovator who invented microprocessor in the early 1900s. Hoff started co-invented things while he was pursuing a PhD. But, in 1968, his life completely changed its course and became a roller-coaster ride, when he was approached by Robert Noyce, co-founder of Intel Corp.
Early Life and Education of Hoff
Marcian Hoff was born on 23rd October 1937 in Rochester, New York. He was lured by the scientific world from a very young age, especially when he received a subscription to Popular Science from one of his uncles at the age of 12. For his undergraduate degree, Hoff went to Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and graduated in 1958 with a bachelor’s degree in Electrical engineering. As an undergraduate student, he worked at Rochester’s General Railway Company during the summer breaks. During his time in this company, he worked with magnetic cores and transistors, and also developed his first two patents during this time.

After completing his college, Hoff received a National Science Foundation Fellowship which gave him the opportunity to attend Stanford University. In 1959, he received an MS degree and a PhD from the same university in 1962. During this time, he co-invented least mean square filter with Bernard Widrow, his guide and a professor of Stanford University. The algorithm they invented is still used in modems today.
Hoff chose to stay in Stanford to carry out his studies on neural networks and integrated circuits, hence, continued research for another four years. While he was learning about integrated circuits, he realized how hard it was to build one.
During this time, Noyce was hiring for Intel, and he contacted a professor of Stanford to know if there was anyone in the campus who had the potential to become an Intel employee. And this is how Hoff ended up as Intel employee in 1968.
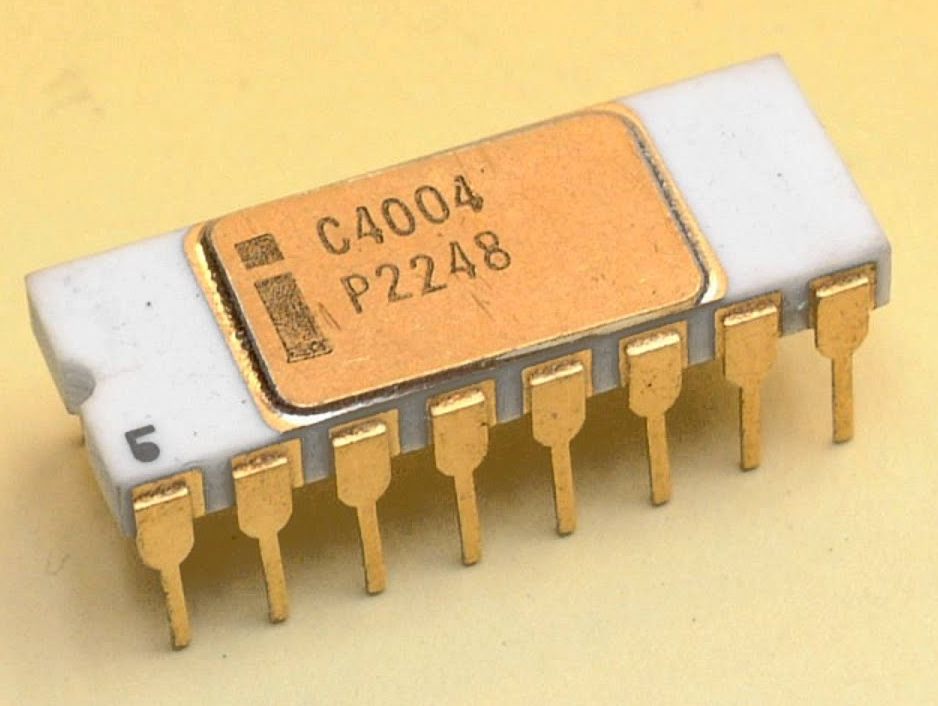
Intel 4004
Marcian Hoff joined Intel in 12th September 1968, as the company’s twelfth member. Intel was established with the main goal to replace all the magnetic core memories with semiconductor memories. Since, it totally diverted from the conventional idea about computer memory, creating a market demand was very tough. So, they decided to take up clients and develop memories as per their requirements. Intel’s first customer for this semiconductor memory was a Japanese company who sold calculators under the name Busicom.
They demanded different types of chips for performing various activities, and hence, both the companies signed a contract to create these chips in April 1969. After this contract, engineers were sent from Japan to work on this design, but at the same time, Hoff on behalf of Intel created another design, which used DRAM (dynamic random access memory). The company liked Intel’s approach better, as a lesser number of chips were able to perform more functions.
Intel, after successfully designing product for this client, wanted to expand the utility of silicon gate, and they hired Dr Faggin in April 1970 to conduct research and make progress on this area. Today, this metal oxide silicon (MOS) process is extensively used in what we call embedded system.
Hoff said that nobody in the company expected as much growth as took place in the following years.
What after Intel 4004 project?
After the 4004 project, Noyce’s next target was to implement their MOS technology in telephony. So, Hoff started working CODEC (a decoder working used in the telephonic industry to convert analog signals to digital and vice versa). Intel was able to come up with monolithic CODEC which could be used commercially.
Hoff left Intel in 1983 and joined Atari as it was working on some really advanced ideas. But, the business strategies of the company were very poor, which resulted in the dropping of the revenue from $2 billion to $1 billion within a single year. Hoff left Atari in 1985 when the company was sold.
From Engineering to understanding Business
Today, Hoff is the part of Teklicon, a company that deals with business and law; established by Gary Summers, who was the head of semiconductor designing in Atari, when Hoff joined the company.

Annasha Dey is an NIT student, who apart from studying engineering is also a content writer. She has a great interest in photography, writing, reading novels, and travelling as well. She is a foodie who loves socializing and hanging out with her friends. She is also a trained Kathak dancer and a big fashion enthusiast. Dey also loves watching TV series, which includes F.R.I.E.N.D.S. and Big Bang Theory. To be a better writer she prefers to read more