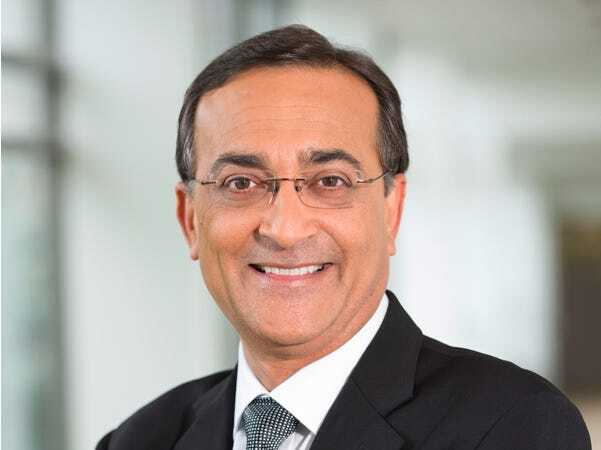
Ajay Bhatt- The inventor of USB who prefers to stay away from limelight
Technology and inventions are important that ultimately helps the community in several ways. When it comes to technology and invention Indian are in top place. Indians and Indian origin persons are well known for human intelligence all over the world. From Google’s CEO to CTOs of many international companies are either Indian or Indian origin. As well, there is a long list of Indian inventors, but not all of them prefer to come in limelight. Yes, such great persons exist, and Ajay Bhatt is one of such personalities. An Indian inventor who changed the scenario of connectivity with USB invention. It became a standard in which one could be used across devices. As well, he dedicated his time to make it acceptable worldwide. Here is an inspiring journey of Ajay Bhatt who made our lives easier with USB invention.
Early life
Ajay Bhatt came in the world in the world on September 6, 1957. He spent early childhood at his birthplace Baroda. Bhatt attended the Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda for graduation. Thereafter, he shifted to New York and completed his Master’s degree there.
Career
Ajay Bhatt has been working with Intel for a long time. In fact, he offered great service and helped Intel in many ways. He joined Intel in 1990. During the early days of his career, he worked as a senior staff architect where he worked in Folsom with a chipset architecture team. At Intel, he was one of the inventive employees and named more than 130 patents including the US and International level parents. Due to his outstanding work, he named an Intel Fellow. As well, he leads the Intel project for next-generation client platform architecture.
The rest of this, he also nominated to take apart as a lecturer in the reputed University of US and Asian region.
The Backstory of Inventing USB
We know that almost all inventions are born out of a need to make the thing easier and feasible. A similar thing happened in this case also. Ajay Bhatt’s wife wanted to print some letters for his daughter’s school project. But that time doing this task was not as easy as it is today. His wife tried several ways but nothing worked and she couldn’t print the letters by herself. Because though computers made an entrance, the peripheral connectivity was still not as advanced as it is today.
That time, the idea pops into his mind to invent such things that can make these tasks easier as well as can be used as a standard for all kind of computer hardware. And USB is a result that now globally accepted and used across the devices.
Importance of Ajay Bhatt’s invention
Of course, computers were the center of attraction in the 90s era. But there was a problem that the user had to use the same company peripheral devices as of the company of computer. That means different components were useless for different company’s devices. Along with Intel, Bhatt solved this problem with USB invention. It became a standard in which one could be used across devices. As well, he dedicated his time to make it acceptable worldwide. Also, the overall price of the computer is lessened, as the USB connected peripheral could be produced at a low price.
Achievements and awards of Ajay Bhatt
Ajay Bhatt has a great contribution to developing many technologies that are accepted worldwide. Includes, accelerated graphics port, Universal Serial Bus i.e. USB and PCI Express. He holds 132 international and U.S. patents as well, dozens of others are in filing stages. In 2002, he honored with achievement in excellence award for his dedication and contribution to the development of PCI express.
Bottom Line
Despite discovering such useful technologies, Ajay never tried to come in limelight. In fact, he could sell his idea for big money. But when Bhatt discovered it, he was working with Intel and never demand financial windfall for game-changing discovery. Today, his invented USB is used as a standard on the planet. As well, we can use different peripheral devices to our PC as per our preferences. It means we can choose the printer of a different company, the mouse of another company and keyboard of another one, totally depends on our choice.
With the thought of solving the technical problem of his family, Bhatt solved the problem of the whole world. USB invention definitely helped to promote computerization and enable us to use any company’s device irrespective of the company of our computer.

Jayshri is an Electronics Engineer, but her passion towards writing made her to be in this field. Apart from content writing, she loves reading, writing and surfing on various topics. In her free time, she likes to watch TV series and news. Sherlock Holmes is her all time favorite show. Jayshri loves cooking various Indian-western dishes.