Apple Restricts iPhone AirDrop With Everyone to Just 10 Minutes in China
Version 16.1.1 of Apple’s iOS has an unusual update in China that hasn’t been implemented in other countries. Apple has restricted AirDrop sharing for users in China to 10 minutes in the latest iOS update. In essence, this implies that Apple users in China cannot use AirDrop for an infinite period of time.
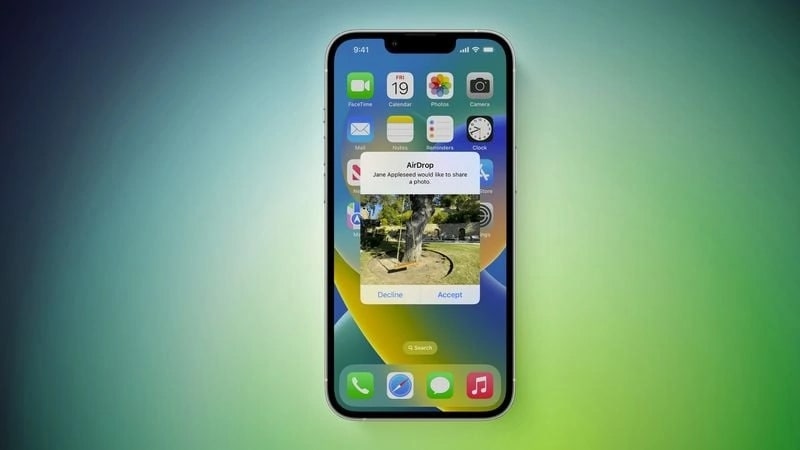
Users can still share files without being constrained by the update, but the 10-minute time limit may put some people off using AirDrop services.
After demonstrators in China used the tool to distribute photographs critical of the Chinese government, Apple has imposed time limits on AirDrop sharing across iPhones.
For users in China, the “Everyone” button in Airdrop is currently restricted to a ten-minute duration. AirDrop’s device-to-device sharing will revert to “Contacts Only” once the ten minutes have elapsed, making it more difficult to systematically send content to random strangers. Just a few weeks after it was utilized to disseminate posters critical of President Xi Jinping, Apple has implemented these additional time limitations to AirDrop.
AirDrop is one of the few unrestricted communication channels in China. Although Apple hasn’t explicitly said this is the motive for the move, the corporation has previously customized its products specifically for the Chinese market.
Read More: Google One VPN Service Now Available on Windows and Mac
According to Bloomberg, AirDrop has frequently been utilized as a fix to circumvent China’s stringent online censorship. That doesn’t mean, though, that AirDrop is a haven for free speech since the tool has also been abused to ground aircraft with fictitious terrorist threats, send nude photos to random people, and, send nude pictures to ground aircraft.
Apple has already come under fire for making adjustments intended to please the Chinese government, including banning VPN apps and concealing the Taiwan flag emoji for customers in Hong Kong and Macau.
Users of Apple devices, like iPhones and iPads, can wirelessly transfer files to other device owners using AirDrop. Peer-to-peer Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy are both used for transfers. Users must explicitly modify AirDrop’s default option of “Contacts Only” in order to get files from “Everyone.”
It’s common for Apple to implement regional limits in order to follow local laws. For instance, the company has not enabled satellite connectivity on the iPhone 14 in India. Due to requirements for hearing protection, users cannot surpass the EU Volume Level in EU member states, for instance.
Apple has a history of enforcing stricter regulations in China for content-related services, like games and podcasts, an area that the national government heavily regulates.
According to Techcrunch, some Weibo users in China believe Apple should impose a 10-minute time limit on all devices worldwide because many people forget to switch off AirDrop. Users who keep it enabled to run the risk of receiving unwanted media files. It is still unknown whether Chinese Android rivals Xiaomi, Huawei, and Oppo would likewise restrict their own sharing services akin to AirDrop in response to government pressure.
Apple has maintained its supremacy in China despite the growth of regional rivals like Oppo and Huawei, especially among more wealthy groups. According to Counterpoint’s analysis, iPhones made up 13% of smartphone shipments in China in the second quarter, falling from 18% and 22% in the first and fourth quarters, respectively.

I am a law graduate from NLU Lucknow. I have a flair for creative writing and hence in my free time work as a freelance content writer.










